Figure 1: Supply curve of labour
Now that a previous column has succinctly explained production functions, the present column will present several macro-economic growth models from the book Mathematical models of economic growth1 of the well-known Dutch economist Jan Tinbergen. A relation will be derived between the growth rates of the economic variables (capital, labour, technical development). The starting point is the Cobb-Douglas production function. The situation with complementary factors is also studied.
In the mentioned column it is stressed, that production functions contribute little to the theoretical insight at the macro level of the economy. The arguments in the present column are outdated from a scientific perspective, and are merely important for historical reasons. It would be unfair to reproach Tinbergen with his theoretical error. Its undermining, notably the theory of Sraffa, was not published until 1960, two years before the publication of Mathematical models of economic growth. In 1962 the theory of Sraffa was still controversial. For instance, between 1962 and 1966 the famous North-American economist Paul Samuelson tried in various ways to refute the theory. He did not succeed2.
It is understandable that Tinbergen retains the then common economic growth models, which have been developed, among others, by the English economist Roy Harrod. Then Tinbergen already specializes in the analysis and development of methods and instruments for economic planning. His interest concerns mainly the practical applications and the policy formulation. The models in the present column are limited to an economic system with one productive sector, however with various scarce production factors. Therefore they offer more flexibility than the one-sector models, which have been presented in a previous column, and merely follow the development of the factor capital.
The models of Tinbergen use merely two production factors, namely the capital K and the labour L. Besides they take into account the technical progress, which advances with time. Tinbergen wonders how these factors affect the growth of the domestic product Y 3. Then the choice for the popular Cobb-Douglas function is obvious4
(1) Y(t) = A(t) × Lλ × Kμ
In the formula 1 the term A(t) takes into account the technical progress. It is sometimes called the total factor productivity. The parameters λ and μ are constants. The same gross product can be generated with various quantities of capital, due to the substitution of K and L. In this model the capital coefficient κ = K/Y is variable, contrary to the Harrod-Domar models. That is a crucial difference. In fact the presented model is similar to the growth model of Solow. Solow uses a linear-homogeneous production function, which is somewhat more general than the Cobb-Douglas function.
Cobb-Douglas production functions have the special property, that they can describe both the Hicks- and Harrod-neutral progress. The form in the formula 1 is Hicks neutral. However, it can be rewritten as Y = (A1/λ × L)λ × Kμ, and that form is precisely Harrod-neutral. Often A(0)=1 is assumed. Tinbergen prefers A(t) = (1 + gA)t, where gA is a constant. Note that for this case the growth rate (∂A/∂t) / A is apparently equal to the natural logarithm ln(1 + gA). Therefore, for a sufficiently small value of gA this quantity approximates the growth rate of A.
In the present paragraph it is assumed that μ = 1 − λ. Then the production function is linear homogeneous, and the productivity does not depend on the chosen scale. It is true that Tinbergen recognizes that the separate enterprises commonly profit from an increased scale, but he assumes that this effect is cancelled at the level of the national economic system as a whole. Next the factor prices are equated to the marginal productivities, that is to say, pL = ∂Y/∂L en pK = ∂Y/∂K. The loyal reader knows from the mentioned column, that this assumption is actually faulty, since here Y and K are aggregated quantities. It can naturally simply be assumed, that these relations still hold (for what it is worth)5.

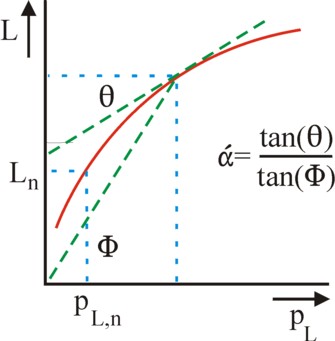
Let the normal price of labour be pL,n, and suppose that then the professional population has a size Ln. When the price changes to another value pL, then the willingness to work will change accordingly. Suppose that this behaviour obeys the formula
(2) L = Ln × (pL / pL,n)α
In the formula 2 α is a constant, which is called the elasticity of the labour supply. The figure 1 is a graphical presentation of the formula 2. Apparently one has α = tan(θ) / tan(Φ), where θ is the slope of the supply-curve of the factor labour, and Φ is the slope of the line through the point (pL, L) and the origin.
In the figure the elasticity α has a positive value, but she can be negative as well. In that case the labour supply decreases, according as pL (the wage level) rises. In that sense the supply curve of labour is no more self-evident than the demand curve of labour. In an identical manner a formula can be stated for the factor capital:
(3) K = Kn × (pK / pK,n)β
The option of the elastic supply adds an element, which is missing in the model of Solow. A special case of the formulas 2 and 3 occurs, when the supply elasticities α and β are zero. Namely, then the supply of K and L will always be equal to Kn and Ln, the quantities which belong to the normal factor prices. The corresponding supply curve in the figure 1 is a horizontal line. This assumption of a completely inelastic supply will be made in the present model, at least for the moment. Then one finds for K the usual relation
(4) ∂Kn / ∂t = σ × Y
Here σ is the constant savings rate. The formula is based on the assumption, that all savings are invested.
The formula 4 shows, that the factor capital grows with time. That growth is caused partly by the natural population growth:
(5) Ln(t) = Ln(0) × (1 + gL)t
In the formula 5 gL is apparently approximately equal to the growth rate of Ln. Moreover, the normal price of the factor labour can increase, because due to A(t) the number of effective labour-hours increases. That will increase the productivity per worker. This development leads to
(6) pL,n(t) = pL,n(0) × (1 + gp,L)t
However, since this model assumes a completely inelastic supply, at least for the moment, the formula 6 is superfluous. Tinbergen even believes, that the supply of capital will always be completely inelastic (β=0), so that the formula 3 can be ignored again6.
Now all formulas are available for the calculation of the relations between the various growth rares. The formula 1 can be inserted into the formula 4, using the formula 5. Thus one finds a first order differential equation in Kn(t), which can be solved in a straightforward manner7. The result is the solution
(7) Knλ = Kn(0)λ + λ×σ × Ln(0)λ × { ((1 + gA) × (1 + gL)λ)t − 1 } / (gA + λ×gL)
Tinbergen justly states, that this behaviour of K is less simple than the common statistical methods suggest. It is striking that the initial state at t=0 determines the later development. The formula 7 yields an important building stone for the analysis of the relation between the growth rates.
A popular trick is to rewrite the growth rate as gY = (∂Y/∂t) / Y = ∂(ln(Y)) / ∂t, where ln() is the natural logarithm function. Apply this trick to the Cobb-Douglas function in the formula 1, then one finds
(8) gY = ln(1 + gA) + λ × ln(1 + gL) + (1 − λ) × (∂Kn / ∂t) / Kn
If desired, the first two terms can be rewritten by means of the approximation ln(1 + x) = x + O(x²), at least for small growth rates. The last term in the right-hand part of the formula 8 is simply the growth rate of capital gK.
Since gK varies with time, gY is also a functiom of t. For t=0 the formula 8 takes on the form gY(0) = gA+ λ×gL + (1 − λ) × σ × (Ln(0) / Kn(0))λ. It is also possible to combine the formulas 1 (still with μ = 1-λ) and 7 in order to calculate the behaviour of the capital coefficient κ=K/Y. Note that for large values of t Knλ approaches λ×σ×A × Lnλ / (gA + λ×gL). Therefore in the limit of t→∞ one has
(9) κ = λ × σ / (gA + λ×gL)
Apparently in the long rung the capital coefficient does become a constant. Note that in the absence of technical progress (that is to say, for A=1) the formula 9 reduces to the Harrod-Domar relation κ = σ / gw. This completes the foundation of the growth model of Tinbergen. On p.36 of Mathematical models of economic growth it is also shown, that the growth rates of K, L and Y can be calculated even for the case, when the labour supply is not perfectly elastic. A table gives the growth rates in situations, where λ=¾ and the elasticity has values of α = -1, 2 and infinity. In those cases the growth rate gp,L of the normal price pL,n of labour from the formula 6 also emerges in the table. She affects the other growth rates.
In the preceding paragraph the growth model of Solow, which has already been published in 1956, has been mentioned several times. Indeed the question arises, what the model of Tinbergen adds to that model. According to the model of Solow a warranted growth occurs, as soon as gY = gK = gA + gL is satisfied. The first identity returns in the described model, where according to the formula 9 Y and K are proportional. Next the second identity can be derived from the formula 8, at least in the form
(10) gY = (gA / λ) + gL

In the growth model of Solow the factor λ does not appear, because he employs a production function of the form λ Y = F(K, A(t) × L). Tinbergen has placed A(t) before the F- function. Furthermore, Tinbergen calculates the time behaviour of the system by means of the formula 7. Solow prefers to express the formulas in terms of the capital intensity k = K / (A×L), and then shows that the system will move towards a state with a constant k.
Furthermore, Solow advances a step further than Tinbergen, because he analyzes a state, where the consumption per worker will be maximal. From this situation he derives his Golden Rule of capital, which dictates the optimal savings rate σ. Tinbergen omits this approach, perhaps because he does not trust her. His argument is explained in a previous column. In short, the policy maker would be obliged to maximize both the present consumption and the consumption of future generations. Here he would have to weigh the interests of succeeding generations.
And finally Tinbergen attaches value to the presence of the elasticity α of the labour supply in the model. For, besides the optimal consumption the maintainance of the full employment is also one of the policy goals. The policy makers can steer the employment by restricting the wage development pL,n. When α is positive, then according to the model the growth of the wage will inhibit the production and the employment. Tinbergen illustrates this by means of the mentioned table, with values of α between 2 and infinity. On the other hand, when αis negative (α=-1 in the table), then the wage rise turns out to stimulate the economy.
The book does not explain the calculations of the quantities in the table. It is clear that the formula 6 predicts a rising pL,n. Thus in the formula 2 the value of pL/pL,n will fall, which may decrease or increase the quantity L, depending on the sign of α. Note that here Ln will obey the formula 5. Besides, according to the model more savings almost always further the growth. Considering the theories of Sraffa and Keynes these policy recommendations must of course be used with care!8
Following Solow, Tinbergen points out, that the labour productivity is given by ap = Y/L = A × (K / L)1-λ = A × k1-λ. She increases according as the capital intensity rises, at least as long as λ<1, which is the normal situation. In case of a rising k and constant factor prices pK and pL the model makes the surprising prediction, that the share of capital in the national income will rise. See also the footnotes.
Another form of technological progress occurs, when the exponent λ of the Cobb-Douglas function will change. One has λ = (∂Y/∂L) / (Y/L). Since the presented model assumes that pL = ∂Y/∂L, apparently one has L×pL = λ×Y. In other words, the share of the factor labour in the national income will fall, when the technological changes lead to a lower value of λ.
The exponent lambda; is sometimes called the production elasticity of the factor labour. It is desirable, that the change in λ will lead to a larger national product Y. Suppose that the change in λ is dλ, then Y will change with a multiplication factor (L/K)dλ = 1/kdλ. Apparently, for a positive dλ one wants k<1, and for a negative dλ one wants k>1. In a table Tinbergen gives the development of the growth rates for the case λ(t) = λ(0) + Λ×t, where Λ = dλ/dt is a constant9. There is more latitude, when the requirement μ = 1 − λ is abandoned. According to Tinbergen the statistical data show, that for a long time λ has hardly changed, which has the consequence, that the distribution of the national income between the factors capital and labour has also been stable.
Finally p.45 and further in Mathematical models of economic growth briefly describe the situation, where no substitution of production factors occurs. In that case there is no continuous production function, but merely a discrete number of production techniques. In a previous column this is called a production process with complementary factors. Incidentally, this situation does not occur frequently. An example is the weaving of cotton in India, half a century ago, which was done both at home on simple weaving-looms and by means of machines10.
Suppose two techniques are available, numbered 1 and 2. Suppose that the technique 2 is most capital-intensive, so that one has k2 > k1. Suppose that the professional population has a size Ln, and the capital stock is Kn. Finally, suppose that one has Kn / Ln < k1. In this situation there is an excess of labour, so that in principle the wage level can become arbitrary low (the "reserve army of unemployed"). A minimum wage pL,n must be introduced in order to prevent the starvation of the workers.
A sound policy will take care that the capital stock Kn increases faster than the population. At a certain time the relation Kn / Ln = k1 will hold, so that all available labour is employed. Now the wage level is no longer zero, but indeterminate. When Kn grows even further, the technique 1 will no longer be satisfactory, because she would leave some capital unemployed. The socially applied production technique becomes a mixture of the techniques 1 and 2. In fact during this phase the substitution of production factors is possible. The reader can find a careful analysis of this phenomenon in the column about the substitution of the means of production in the theory of Sraffa, a five-finger exercise of your columnist. In another column the same phenomenon is explained by means of the theory of algebraic sets.
In this phase of substitution isoquants can be drawn. In fact these are the curves of technological possibilities. Tinbergen states, that in this situation both techniques will evidently pay the same price pK,n for capital, and for pL,n as well. Assuming that one has pK,n = (Y − pL,n×L) / K for both techniques, one can calculate in a straightforward manner that
(11) pL,n = (k2×ap1 − k1×ap2) / (k2 − k1)
In the formula 11 api is the labour productivity of the technique i. Apparently, now the wage level is fixed.
According as the stock of capital Kn keeps growing, more of the technique 2 must be applied, at least as long as full employment is desired. Finally, Kn will have grown so much, that even the technique 2 can no longer absorb all capital. Here the situation occurs, where the market price pK,n will become arbitrary low. This phenomenon is not purely fictitious, because both Karl Marx and John M. Keynes predict the fall of the interest rate in the long run.